What is Business Process Management (BPM)?
BPM Lifecycle: The 5 Steps in Business Process Management
What are the Various Types of BPM Systems?
What are the Benefits of Implementing BPM?
When should Organizations Implement BPM?
What is Business Process Automation (BPA)?
Implement Process Automation at Scale with HappyFox Workflows
Business process management (BPM), as defined by Gartner, is a discipline that uses various tools and methods to design, model, execute, monitor, and optimize business processes. A business process coordinates the behavior of people, systems, information, and things to produce business outcomes in support of a business strategy.
BPM focuses on putting a consistent, automated process in place for routine transactions and human interactions. It helps to reduce the business’s operational costs by decreasing waste and rework, and by increasing the overall efficiency of the team.
Organizations engaged in BPM can choose to follow one of the various BPM methodologies, which include Six Sigma and Lean.
BPM is not a software product. There are BPM tools available that help in implementing standard and automated business processes. For example, HappyFox Workflows helps businesses automate complex, multi-step, and repetitive business processes. BPM, however, is not a software product in itself.
BPM is not Task Management. Task or Project Management is about handling or organizing a set of activities. A project management software like Microsoft Project, Jira, Asana, or Trello helps in managing tasks and ad-hoc projects. Business Process Management, on the other hand, is focused more on repetitive and ongoing processes that follow a predictable pattern or process management.
BPM systems can be categorized based on the purpose that they serve. Here are the three types of business process management:
This type of business process management system handles processes that primarily depend on existing business systems (e.g., HRMS, CRM, ERP) without much human involvement. A system-centric business process management software has extensive integrations and API access to be able to create fast and efficient business processes. An example of an integration-centric process is online banking, which can include different software systems coming together.
Human-centric BPM considers the people first, supported by various automation functions. These are processes that are primarily executed by humans, and automation does not easily replace them. These often have a lot of approvals and tasks performed by individuals. Examples of human-centric processes include providing customer service, handling complaints, on-boarding employees, conducting e-commerce activities, and filing expense reports.
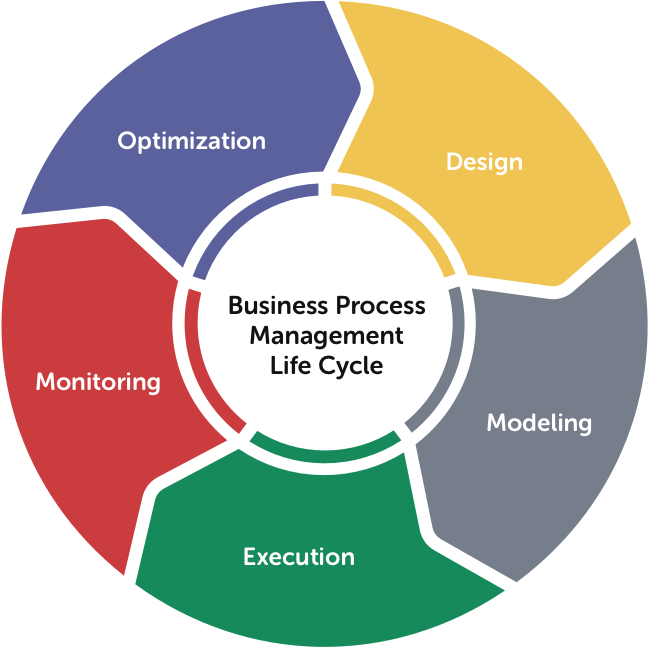
Business analysts review current business rules, interview the various stakeholders, and discuss desired outcomes with management. The goal of the process design stage is to gain an understanding of the business rules and ensure if the results are in alignment with the organizational goals.
Modeling refers to identifying, defining, and making a representation of new processes to support the current business rules for various stakeholders.
Execute the business process by testing it live with a small group of users first and then open it up to all users. In the case of automated workflows, artificially throttle the process to minimize errors.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and track metrics against them using reports or dashboards. It’s essential to focus on the macro or micro indicators – an entire process vs. process segments.
With an effective reporting system in place, an organization can effectively steer operations toward optimization or process improvement. Business Process Optimization (BPO) is the redesign of the business processes to streamline and improve process efficiency and strengthen the alignment of individual business processes with a comprehensive strategy.
Business Process Management helps organizations move toward total digital transformation and help them realize bigger organizational goals. Here are some of the key benefits of using BPM in your business:
1. Improved Business Agility: Changing and optimizing an organization’s business processes is necessary to keep up with the market conditions. BPM allows organizations to pause business processes, implement changes, and re-execute them. Altering workflows, as well as reusing and customizing them, enables business processes to become more responsive and gives the organization deeper insights into the effects that process modifications have.
2. Reduced Costs and Higher Revenues: A business process management tool eradicates bottlenecks, which significantly reduces costs over time. An effect of this can be a reduction in lead times for product sales, giving customers quick access to services and products, which leads to higher sales and improved revenue. BPM solutions can also allocate and track resources to reduce waste, which can also reduce costs and lead to higher profits.
3. Higher Efficiency: The integration of business processes brings the potential for end-to-end improvement in process efficiency. With the right information, process owners can closely monitor delays and allocate additional resources if needed. Automation and the removal of repetitive tasks, add to more efficiencies in the business process.
4. Better Visibility: BPM software enables automation while ensuring real-time monitoring of key performance metrics. This enhanced transparency leads to better management and the ability to modify structures and processes efficiently while tracking outcomes.
5. Compliance, Safety, and Security: A comprehensive BPM guarantees that organizations comply with standards and stay up to date with the law. BPM can also promote safety and security measures by properly documenting procedures and facilitating compliance. As a result, organizations can encourage their staff to safeguard organization assets, such as private information and physical resources from misuse, loss, or theft.
Here are some examples of business processes where implementing BPM will result in a high return on investment.
1. Dynamic processes that require regulatory compliance changes, such as a change in customer information management following changes in finance or privacy laws.
2. Complex business processes that require orchestration and coordination across multiple business units, divisions, functional departments, or workgroups.
3. Measurable mission-critical processes that directly improve a crucial performance metric.
4. Business processes that require one or more legacy applications for their completion.
5. Business processes with exceptions that are handled manually and/or require quick turnarounds.
Business process automation (BPA) and business process management (BPM) are related, and in some ways complementary, but they’re not the same. BPA is about automating processes, while BPM is about managing processes, which may or may not involve automation. Simply put, all BPA can be considered to be a form of BPM, but not all BPM may include BPA.
Business Process Automation (BPA) refers to any method that is used to streamline business processes through automation. It can take on a wide variety of applications and tools that aim to achieve gains in productivity, agility, efficiency, and compliance in the day-to-day tasks of a business.
Common examples of processes that benefit from BPA include:
Business processes that are suitable for automation are typically those that are started by a specific, triggering event. For example, the filing of an expense report may trigger a pre-defined series of steps that ends when the employee receiving reimbursement in their bank account.
BPM, on the other hand, is a systematic approach to improving business processes. When it is successfully implemented, everyone understands better how they contribute to the achievement of organizational goals. This generally leads to a happier, more productive workforce, which tends to result in happier customers, higher revenues, and lower costs.
HappyFox Workflows is a business process and workflow automation software that can help you implement better business processes and streamline organization-wide productivity and reduces costs.
Use HappyFox Workflow to reduce repetitive tasks for your employees while ensuring reliable, error-free, and prompt data entry and process standardization. HappyFox Workflows boosts team productivity by cutting down repetitive grunt work, so your employees can focus on more important things of higher business value.
With a drag-and-drop, no-code workflow builder, you can build dynamic workflows with several steps without any coding knowledge. You no longer have to depend on your IT/Engineering team to run costly automation projects.
You elegantly orchestrated business processes involving actions across multiple systems with HappyFox Workflows. HappyFox Workflows integrates with HappyFox Help Desk, Zendesk Support, Salesforce, and more enterprise business applications.
Schedule a demo with us to learn more about how HappyFox Workflows can help implement BPM at your organization.
Talk to someone smart, quickly.